Thermal camera module is mainly used in infrared detectors and infrared cameras to reduce the operating temperature of the detector, thereby improving its sensitivity to infrared radiation and image quality. In many high-end infrared imaging applications, such as military reconnaissance, night vision monitoring, aerospace exploration, scientific research, and some industrial process monitoring, the role of the refrigeration movement in thermal imaging camera modules is crucial.
A thermal module is a compact assembly used in electronic devices to manage and dissipate heat, ensuring components operate within safe temperature limits. These thermal imaging modules typically integrate a combination of heat sinks, fans, heat pipes, or vapor chambers, depending on the device's cooling requirements and spatial constraints. By efficiently transferring heat away from critical components like CPUs, GPUs, and power units, thermal modules play a crucial role in maintaining performance, reliability, and longevity of electronic systems. Such as a cooled thermal camera module or uncooled thermal module, thermal imaging IR camera modules are essential in a variety of applications ranging from computers and servers to automotive electronics and telecommunications equipment, where effective heat management is critical to prevent overheating and optimize functionality.

No, you cannot use your phone as a thermal module in the traditional sense. A thermal module specifically refers to a device or system designed to manage and dissipate heat in electronic and mechanical systems, such as computers and industrial machinery. Thermal imaging IR camera modules typically consists of components like heat sinks, fans, and heat pipes, which are not present in smartphones.
However, some smartphones are equipped with thermal management technology, such as passive heat spreaders or software that throttles performance to reduce heat generation. While these features help manage the phone's internal temperature, they do not transform the phone into a thermal module capable of externally managing heat in other devices.
A thermal module works by efficiently transferring heat away from heat-generating electronic components to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance. The thermal imaging IR camera modules typically consists of heat sinks, fans, heat pipes, or vapor chambers, each playing a role in the heat dissipation process. Heat sinks, made of thermally conductive materials like aluminum or copper, absorb heat directly from the component. Heat pipes transfer the absorbed heat away from the source using the phase transition of a liquid coolant inside. Fans or blowers then help disperse the heat into the surrounding air, while vapor chambers distribute heat evenly across the device. This orchestrated process of the thermal imaging infrared camera module maintains the components at safe operating temperatures, enhancing both performance and longevity.
CNGEIR is your go-to custom optical lens manufacturer and custom optical components supplier in China. Elevate your tech with our world-class IR optics combined with advanced optical materials today!
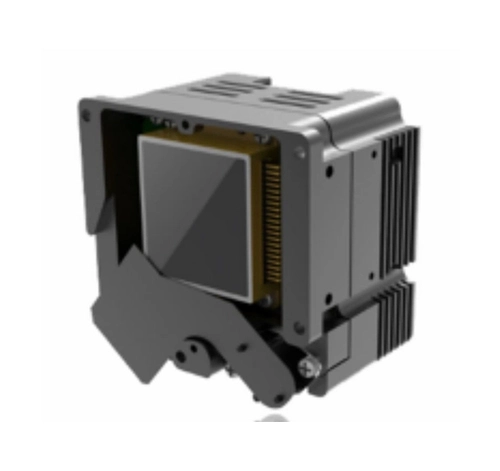


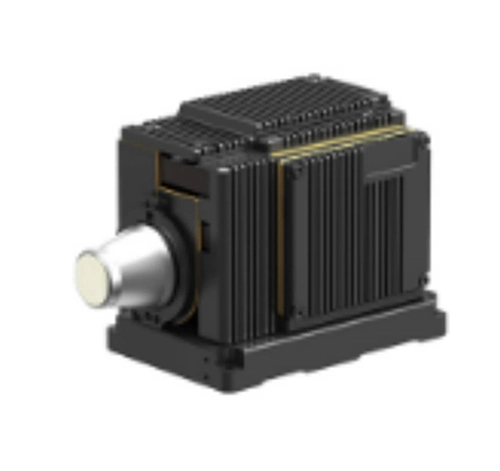
Thermal imaging IR camera modules have a diverse range of applications across various industries and sectors due to their ability to detect and measure infrared radiation, which is directly related to the temperature of objects and surfaces.
Industrial Maintenance and Predictive Maintenance: Detecting hotspots, malfunctions, and potential failures in industrial equipment, machinery, and electrical systems. Monitoring the condition of bearings, motors, transformers, and other critical components
Building Inspection and Energy Audits: Identifying thermal bridging, air leaks, and insulation issues in buildings. Assessing the energy efficiency of buildings and detecting areas of heat loss
Security and Surveillance: Enhancing night vision and perimeter security through the detection of heat signatures. Aiding in search and rescue operations by identifying people and animals in low-visibility conditions
Medical and Healthcare: Assisting in the early detection of certain medical conditions by identifying temperature variations in the body and Monitoring skin temperature for fever detection and circulation issues
Automotive and Transportation: Detecting brake issues, overheating components, and potential problems in vehicles. Monitoring the condition of tires, brakes, and engines for maintenance purposes
Research and Development: Analyzing heat transfer and thermal phenomena in scientific experiments and engineering projects
Conducting non-destructive testing and material analysis
Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring: Detecting plant stress and disease by identifying temperature variations in crops. Monitoring wildlife and their habitats through thermal signature detection
The versatility and non-invasive nature of thermal imaging IR camera modules make them invaluable tools in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and scientific applications, where the ability to detect and measure temperature patterns is crucial for various purposes, from maintenance and diagnostics to surveillance and research.
Thermal imaging infrared camera modules leverage advanced sensor technology to capture and process infrared radiation emitted by objects based on their temperature. At the core of these thermal imaging infrared camera modules are specialized infrared detectors, such as microbolometers or quantum well-infrared photodetectors (QWIPs), that convert infrared energy into electrical signals.
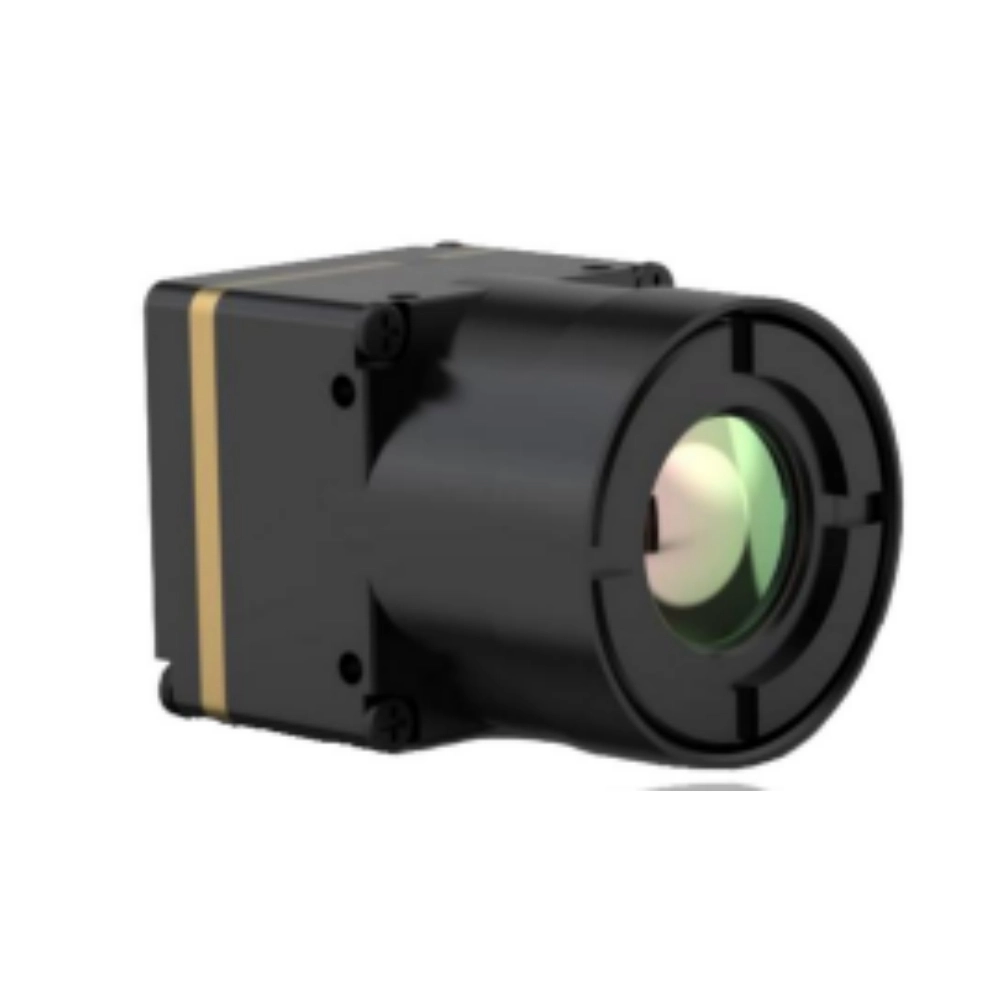
The thermal imaging infrared camera module typically includes optics, such as infrared lenses, to focus the thermal radiation onto the detector array. Integrated electronics handle tasks like analog-to-digital conversion, image processing, and output formatting to produce a thermal image that visually represents the temperature variations across the scene.
Modern thermal imaging infrared camera modules may also incorporate features like image stabilization, digital zoom, and wireless connectivity to enable a wide range of applications from building inspection to industrial monitoring and security surveillance. The compact, rugged, and power-efficient design of these modular units makes them well-suited for integration into various systems and devices where thermal imaging capabilities are required.
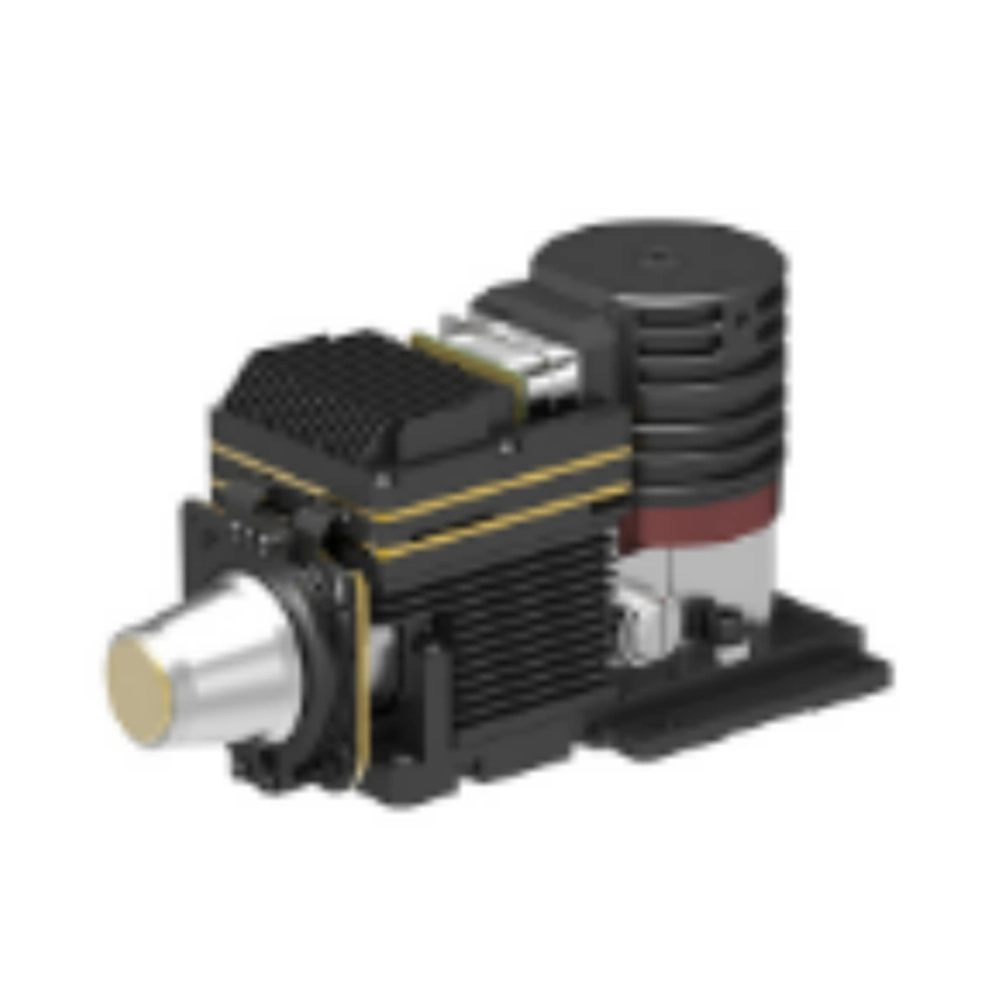
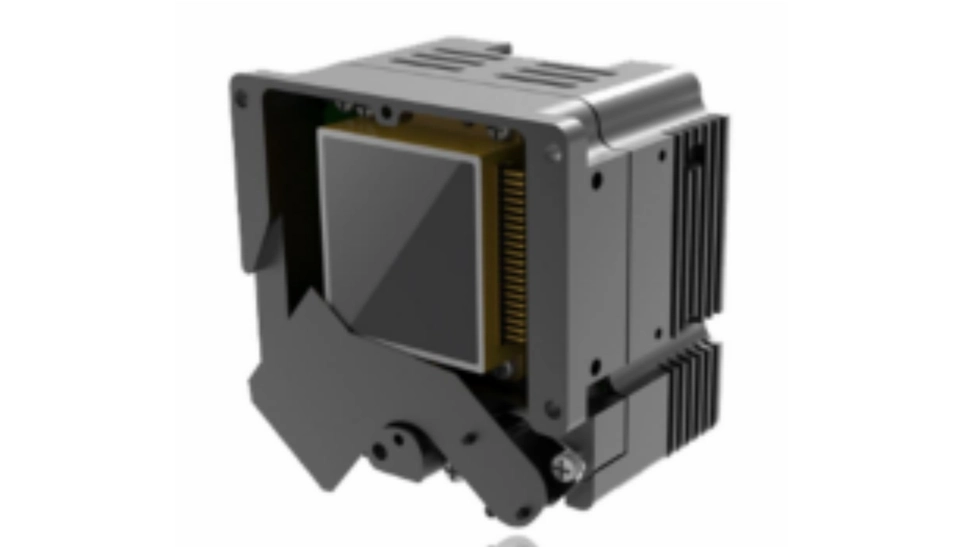


Thermal imaging camera modules can be broadly categorized into cooled and uncooled designs, each offering distinct advantages based on the specific application requirements.
Cooled thermal modules use cryogenically-cooled infrared detectors, typically based on materials like mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) or indium antimonide (InSb), which offer superior thermal sensitivity and resolution but require complex cooling mechanisms like Stirling engines or thermoelectric coolers. This added complexity results in cooled thermal modules being larger, more expensive, and requiring higher power consumption.
In contrast, uncooled thermal modules utilize microbolometer or pyroelectric infrared detectors that operate at ambient temperatures, eliminating the need for bulky and power-hungry cooling systems. While uncooled thermal modules generally have lower thermal sensitivity compared to their thermal modules, uncooled thermal modules offer the benefits of being more compact, cost-effective, and power-efficient, making uncooled thermal modules well-suited for applications where size, weight, and power constraints are crucial, such as in portable, battery-powered devices.
The choice between cooled thermal modules and uncooled thermal imaging modules ultimately depends on balancing performance requirements against practical considerations for the specific use case.
CNGEIR is your go-to custom optical lens manufacturer and custom infrared optical products supplier in China. Elevate your tech with our world-class IR optics combined with advanced optical materials today!
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China