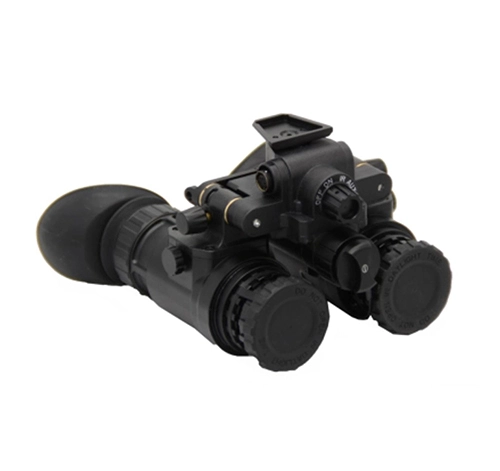
Head-mounted binoculars are a specially designed observation tool that allows the user to observe distant objects through the head-mounted device while keeping their hands free. This type of telescope is especially suitable for situations that require prolonged observation or other activities at the same time, such as bird watching, hiking, watching sports events, and even certain types of work tasks.
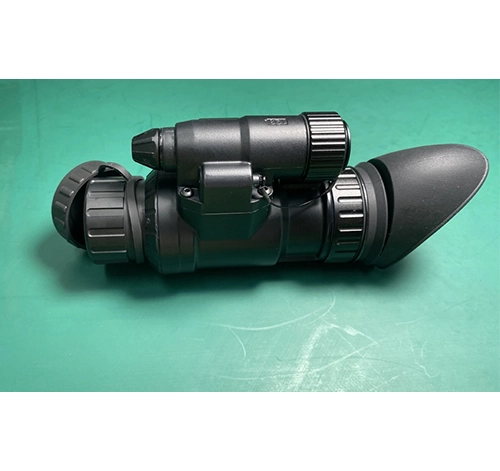
Night vision headgear refers to wearable devices equipped with night vision technology, enabling users to see in low-light or dark conditions. These devices amplify available light, such as moonlight or starlight, converting it into visible images. Commonly constructed with an image intensifier tube that enhances environmental light, night vision headgear is crucial for various nocturnal activities. It’s widely used in military and law enforcement operations for nighttime surveillance and tactical maneuvers. Additionally, it finds applications in wildlife observation, security, and recreational activities like camping and hiking. Night vision headgear provides hands-free operation, crucial for tasks requiring both mobility and visual clarity in darkness.

Night vision headgear operates using image intensification technology that amplifies minimal existing ambient light (such as moonlight or starlight) to make otherwise dark environments visible to the human eye. The core component is the image intensifier tube. Here’s how it works: Photons from available light enter the device and hit a photocathode, which then converts these photons into electrons. These electrons are accelerated and amplified across an electrostatic field towards a phosphor screen. When these electrons strike the phosphor screen, they create a visible image, which is often green because the human eye can differentiate more shades of green than other colors. This process enables users to see in conditions of virtual darkness.
The lifespan of night vision headgear largely depends on the quality of the components, usage habits, and maintenance. Generally, the most critical component, the image intensifier tube, determines the overall lifespan of the device. High-quality tubes can last up to 10,000 to 15,000 hours of active use if properly maintained. Regular wear and tear, exposure to bright lights while in operation (which can burn out the tube), and rough handling can significantly reduce this lifespan. Proper storage and careful maintenance, such as keeping the lenses clean and storing the device in a cool, dry place, are crucial for maximizing its durability and functionality.

 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China