A handheld telescope is a portable optical instrument designed to observe objects at a distance. They are widely used in a variety of activities, including bird watching, hunting, hiking, sporting event watching, astronomical observation and more. Key characteristics of handheld telescopes include magnification, objective diameter, field of view, weight and size.
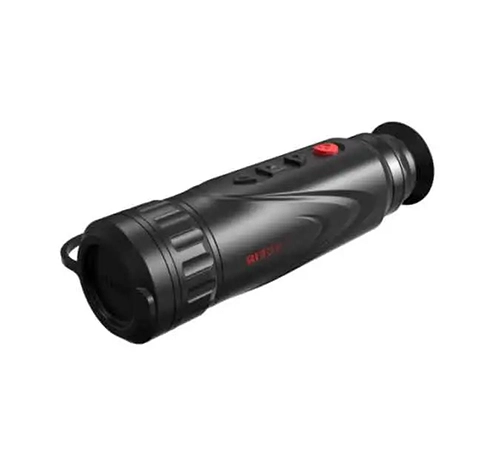
Handheld thermal binoculars are sophisticated optical devices designed for enhanced visibility in various conditions, especially in low light or through obstructions like smoke and fog. Utilizing infrared technology, these binoculars detect heat emitted by objects and convert it into a visible image, enabling users to see warm-bodied creatures and mechanical devices that emit heat, regardless of lighting conditions. Ideal for wildlife observation, security, search and rescue operations, and military applications, handheld thermal binoculars are invaluable for anyone needing to identify and track heat signatures at a distance. Portable and durable, these devices provide a crucial advantage in navigating or monitoring environments where traditional optical binoculars fall short.
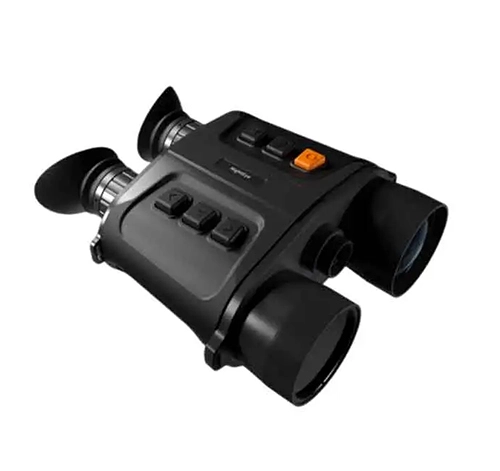

Handheld thermal binoculars are expensive due to several factors that contribute to their high manufacturing costs and sophisticated technology. First, they utilize advanced thermal imaging sensors and optics that are costly to produce, requiring precise engineering and high-quality materials to detect subtle variations in heat. Additionally, these devices incorporate complex electronics for image processing and display, often including features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, digital zoom, and high-resolution displays, which further drive up costs. The rugged design necessary for outdoor use, typically waterproof and shockproof, also adds to the expense. Finally, the niche market and specialized applications for thermal binoculars result in lower production volumes, keeping prices high due to limited economies of scale.
Handheld thermal binoculars and infrared binoculars both operate on the principle of detecting infrared radiation, but they differ fundamentally in their technology and applications. Handheld thermal binoculars detect the mid to long-wave infrared radiation emitted by objects as heat and convert it into visible images, allowing users to see thermal signatures in complete darkness or through obstructions like smoke and foliage. In contrast, infrared binoculars, often referred to as night vision binoculars, require some ambient light (or an infrared illuminator) to enhance the visible light in the scene, making them suitable for low-light conditions but not in total darkness like thermal binoculars. This distinction makes thermal binoculars more versatile for a broader range of conditions, especially where absolute darkness or camouflaged environments are involved.

 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China