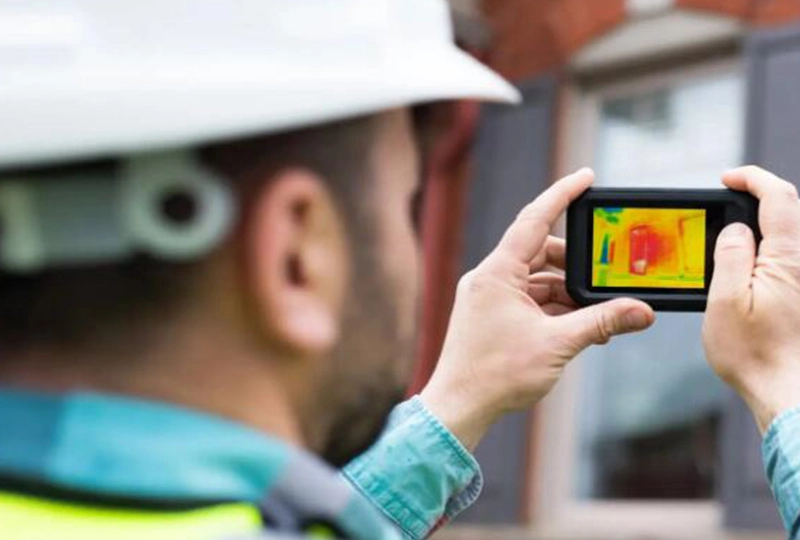
The application of infrared technology in Thermal Imaging Cameras is one of thermal imaging camera's most extensive and important applications. A thermal imaging camera is a device capable of detecting and converting the thermal radiation of an object into a visual image, known as a Thermogram. With heat maps, users can identify and measure the temperature distribution on the surface of objects, allowing them to "see" objects even in complete darkness. This capability makes thermal imaging cameras useful in many fields.
The working principle of thermal imaging cameras
At the heart of a thermal imaging camera is an infrared detector that can detect the infrared radiation emitted by the target object. This infrared radiation is converted into electrical signals, which are then used to generate images through digital signal processing technology. Thermal imaging cameras also typically include an optical infrared system for focusing infrared radiation, and a display screen for displaying the final heat map.
Specific patterns and anomalies in heat maps
In conclusion, the application of infrared technology in thermal imaging has greatly expanded human perception, enabling us to "see" temperature in ways that were previously unimaginable, which has important applications and value in many fields.
Electrical thermal imaging vs. Infrared thermography
Electrical Thermal Imaging: Electrical thermal imaging uses specialized camera sensors that detect and measure the heat generated by electrical components and systems. Electrical thermal imaging focuses on identifying hot spots, overloads, and potential electrical issues within electrical equipment, circuitry, and infrastructure. Electrical thermal imaging is widely used for predictive maintenance, fault detection, and quality control in industrial, commercial, and residential electrical systems.
Infrared (IR) Thermography: Infrared thermography uses cameras that detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects, which is directly related to their surface temperature. Infrared thermography provides a comprehensive thermal map of the entire scene or target, allowing for the analysis of temperature patterns, hotspots, and thermal anomalies. Infrared thermography has a broader range of applications, including building inspections, mechanical system monitoring, medical diagnostics, and environmental studies, in addition to electrical system analysis.
In summary: Electrical thermal imaging is specialized for detecting electrical issues, while infrared thermography has a broader range of applications for thermal analysis and temperature measurement across various industries and domains.
The types of thermographic inspection
Thermography techniques vary based on inspection methods, purposes, data analysis, and timing. Passive thermography captures thermal images under normal conditions, while active thermography uses external heat sources to reveal defects. Electrical thermography focuses on identifying electrical issues, mechanical thermography detects mechanical equipment problems, and building envelope thermography detects heat loss in buildings. Predictive maintenance thermography prevents equipment failures. Data analysis includes qualitative analysis for visual inspection and quantitative analysis for measuring temperature values and defect severity. Timing methods include baseline thermography for creating reference images and thermal trending thermography for monitoring changes over time.
CNGEIR is your go-to custom optical lenses manufacturer and custom optical components supplier in China. Elevate your tech with our world-class IR optics combined with advanced optical materials today!
CNGEIR Hot Recommended Products:
Popular Articles at CNGEIR :

 en
en 



 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
No.9 Zhongxing East Road, Lishui Economic Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China